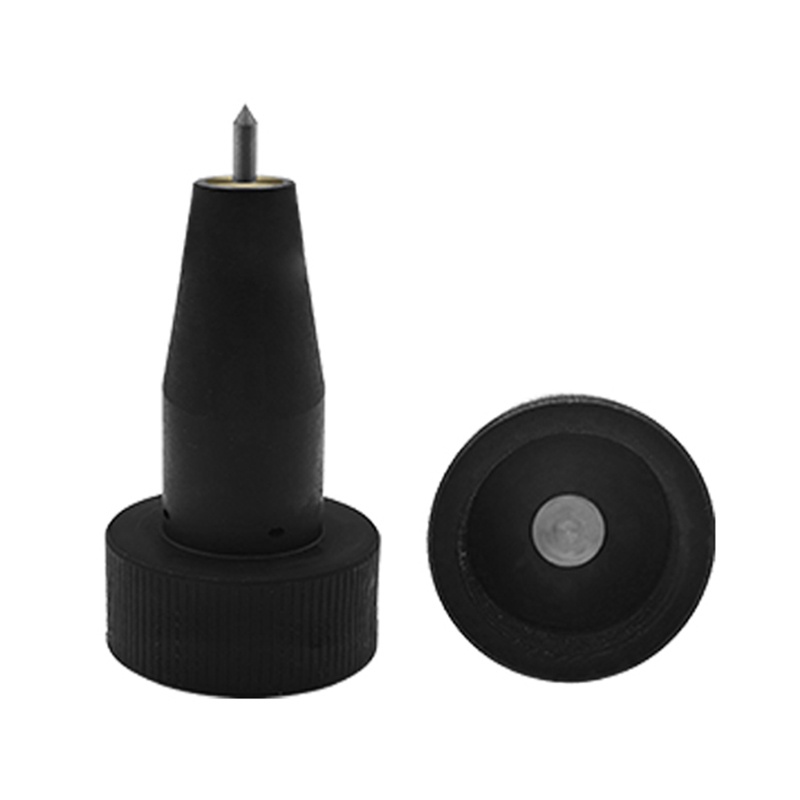
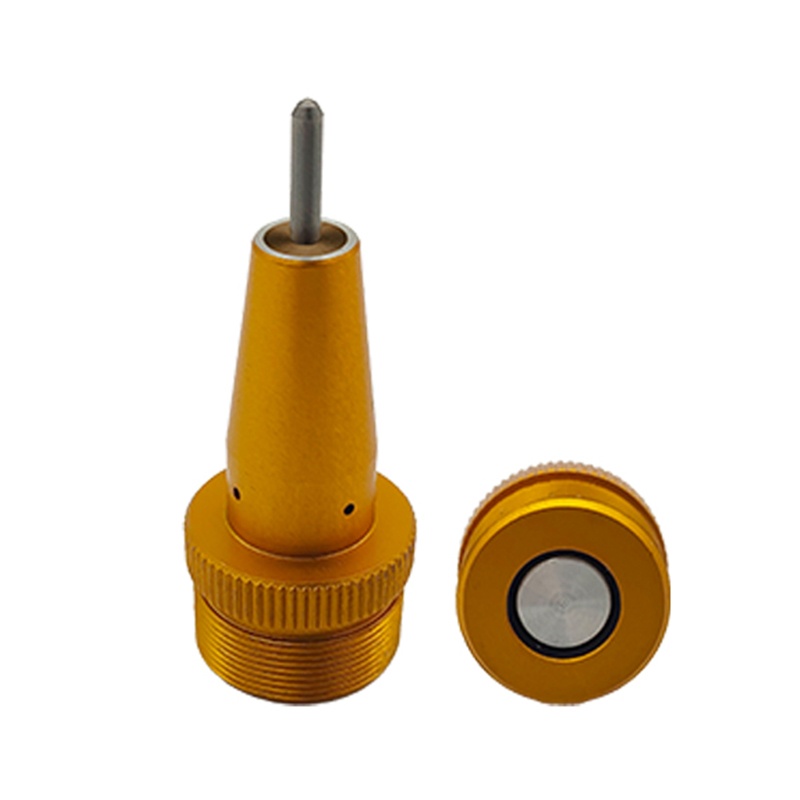
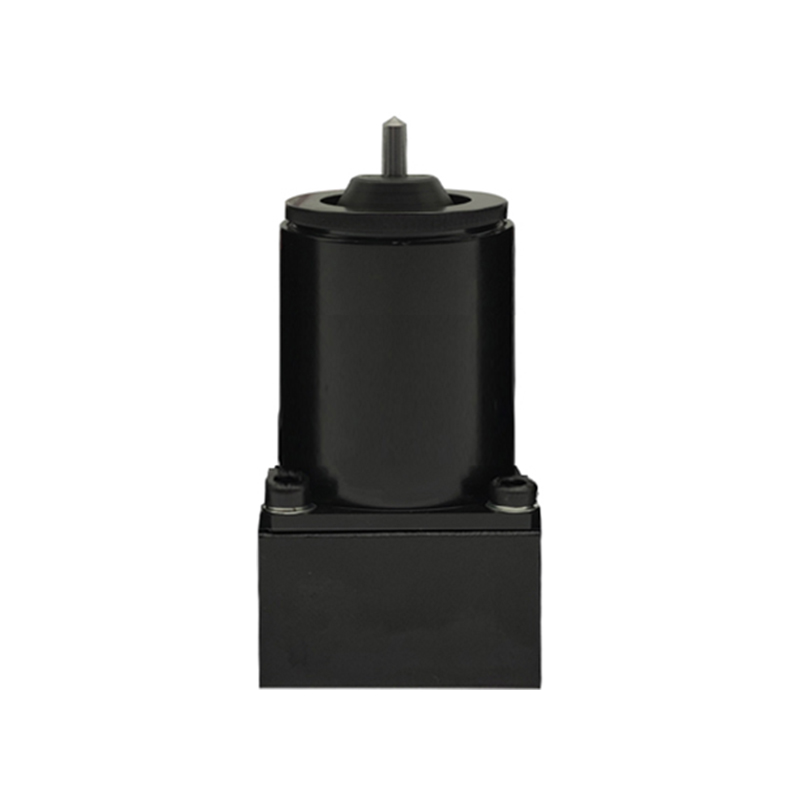
Pneumatic Marking Machine Needle Not Firing? Causes and Solutions
The failure of the marking needle of a pneumatic marking machine to release air is a common fault, which may involve multiple links such as the air source, air path, and control signal. This malfunction may cause production delays, inconsistent marking quality, and increased maintenance costs. Understanding the root cause, following a structured troubleshooting process, and implementing preventive measures are crucial for keeping your marked equipment in the best condition.
In this article, we will explain the working principle of pneumatic marking machines, explore the common causes of needle failures, provide solutions, and share expert maintenance tips.
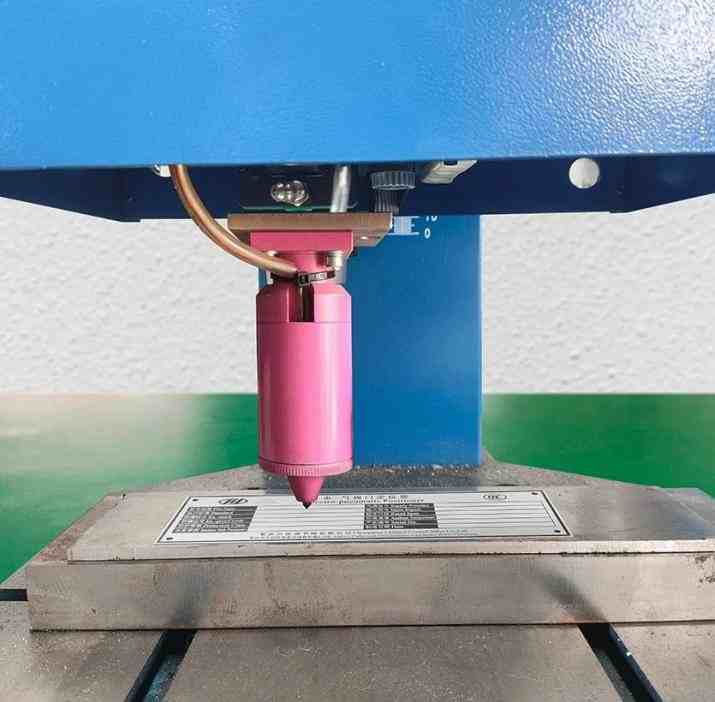

How a Pneumatic Marking Machine Works?
A pneumatic marking machine utilises compressed air to move a marking needle backwards and forwards very quickly. As the needle moves, it touches the workpiece, marking its surface with small dots or lines which, when viewed collectively, form alphanumeric characters or graphics.
The main components include:
- Marking Needle: This is the main component of the marking machine and touches the surface of the workpiece. The marking and its durability will depend on the needle’s material, precision, sharpness, and its overall quality.
- Pneumatic System: This section contains the air compressor, hoses, and valves which supply and regulate the pneumatic air needed to operate the machine.
- Control System: These are the electronics that are programmed to manage the timing, depth, and position of the marking needles’ strikes.
- Mechanical Structure: These are the components that position and move the needle assembly so that the markings will be accurate and executed with precision.
The system as a whole will produce markings that are sharp and of good quality as long as each component is functioning properly. The machine is unable to perform its designated task if the marking needle is unable to fire.
Common Causes of a Needle Not Firing and Their Solutions
A pneumatic marking needle’s failure to operate can be traced to several categories of problems. Below are the most frequent ones and how to address them.
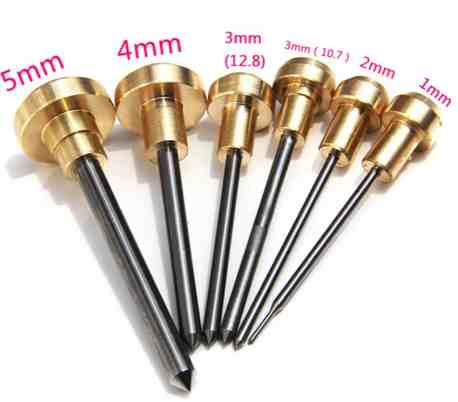

1. Air Supply Issues
- Air Compressor Not Started / Insufficient Air Pressure
- Inspect whether the compressor is functioning correctly and if the output pressure is within the designed limits (typically between 0.4 and 0.6 MPa).
- Solution: Engage the air compressor and modify the pressure output on the compressor to the desired setting; verify the accuracy of the air receiver tank pressure gauge.
- Air Supply Valve Not Open or Damaged
- The main air line or the machine’s inlet valve is closed, or the valve contains internal blockage.
- Solution: Inspect the valve in the air line; diagnose and purge the valve, replacing any inoperative valve components as needed.
- Air Supply Connector Leakage
- Air can escape from quick-connect fittings if the fittings are loose or the sealing ring is worn.
- Solution: Replace sealing rings and try to tighten loose fittings. Check for leaks using soapy water solution.
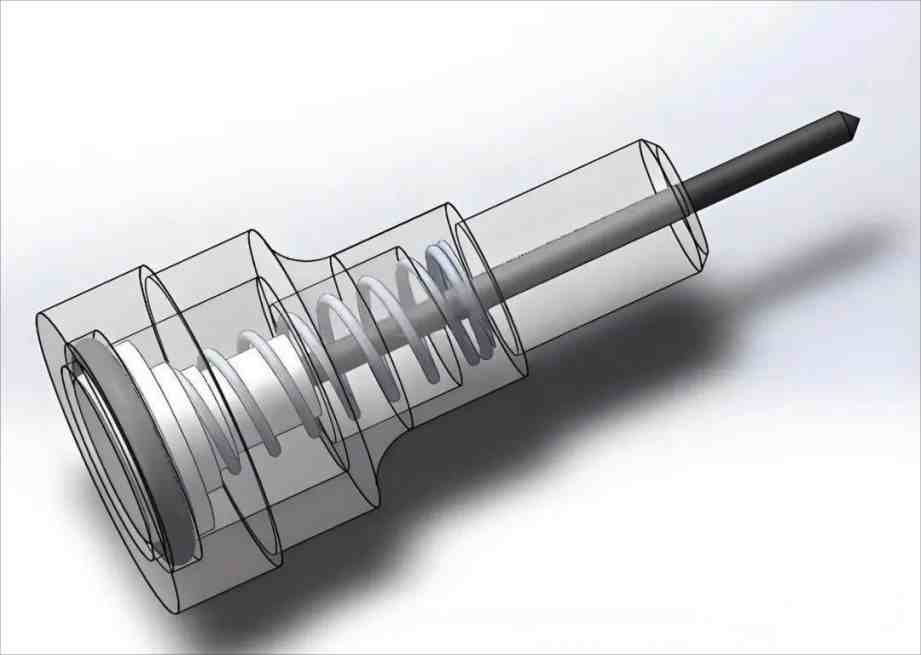
2. Air Circuit Blockage
- Air Hose Kinked or Damaged
- The air hose is flattened, bent, or aged and cracked which restricts airflow.
- Solution: Preferably using pressure-resistant PU tubing, straighten or replace air hose.
- Clogged Filter / Air-Water Separator
- Debris and moisture build up filter, causing blockage.
- Solution: Remove filter element and clean. Drain regularly which is recommended to empty air-water separator once per shift.
- Pressure Regulator Malfunction
- Low output pressure is a result of a damaged or improperly set pressure regulator.
- Solution: Replace damaged regulator and readjust to correct pressure, and check with gauge afterwards.
3. Solenoid Valve Malfunction
- Solenoid Coil Burnout
- Failure to energise and open the valve may be due to an open circuit or short circuit in the coil.
- Answer: Check the coil’s resistance value and change the solenoid coil with an identical one.
- Valve Core Stuck or Blocked
- Movement of the valve core may be slowed or fully immobilised due to contaminants such as oil or rust.
- Answer: Remove the solenoid valve and clean the valve core and body with alcohol. Apply specialised lubricant to the valve body.
- Control Signal Anomalies
- Failure of the PLC or control board to issue the drive signal to the solenoid valve can be problematic.
- Answer: Examine the control parameters, paying attention to the timing for the air circuit’s opening, and check the solenoid valve’s power supply of 24 volts DC with the multimeter.
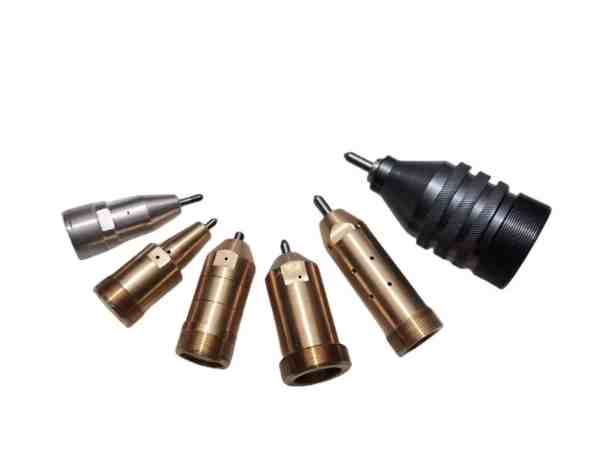

4. Mechanical Component Failure
- Marking Needle Air Port Blockage
- Metal debris or oil contamination clogs the air port of the needle.
- Solution: Disassemble the marking needle and use a fine pin or compressed air to clean the air port.
- Cylinder Piston Seized
- Internal contamination or insufficient lubrication causes the piston to stick.
- Solution: Disassemble the cylinder, remove any debris, and apply pneumatic-specific lubricant.
- Seal Wear or Aging
- Worn O-rings or piston seals result in air leakage.
- Solution: Replace the seals inside the cylinder or solenoid valve.
5. Operational and Environmental Factors
- Incorrect Software Settings
- Air circuit control parameters are not enabled or are improperly configured.
- Solution: Check the air circuit control options in the marking software to ensure that the “air output time” and “trigger signal” settings are correct.
- Low Ambient Temperature
- old temperatures cause condensation inside the air hoses to freeze, blocking airflow.
- Solution: Install an air dryer or add antifreeze to the air circuit.
- Operator Error
- Starting the machine without turning on the air supply, or accidentally pressing the emergency stop button.
- Solution: Standardize operating procedures and train operators to start and stop the machine in the correct sequence.
Systematic Troubleshooting Process
When facing a needle that does not fire, a systematic approach will save time and avoid unnecessary part replacements:
- Check Air Supply First – Verify compressor output, pressure settings, and hose connections.
- Inspect the Needle Assembly – Look for visible damage, wear, or dirt; clean and lubricate.
- Test the Solenoid Valve – Ensure it is receiving control signals and is functioning properly.
- Check Control Signals – Use a multimeter to confirm the control board is sending the right commands.
- Test After Each Step – Make adjustments and run a short marking test before moving to the next step.
This step-by-step method helps identify the real cause instead of replacing multiple parts blindly.
Preventive Maintenance Recommendations
Efforts to prevent faults are always more effective than operational efforts directed at fixing them. The following are recommendations to maintain your pneumatic marking machine and marking needle:
- Regularly Clean Air Filters and Moisture Traps – Prevents contaminants and moisture from entering the pneumatic system.
- Lubricate Moving Parts – Apply the right type and quantity of lubricant to moving components.
- Inspect Needles Frequently – Proactive replacement of overly worn marking needles prior to excessive wear enhances marking quality.
- Monitor Air Pressure – Consistent performance is observed when air pressure is maintained within optimal levels.
- Schedule Routine Servicing – The machine must be evaluated periodically by certified professionals.
Final Thoughts
Failure of a single pneumatically actuated marking needle can stop the clock and incur expensive machine downtime. Knowing the underlying mechanisms of the system, the common recurring issues, and having a step-by-step approach to troubleshooting can help resolve issues in a timely manner and avoid repeated failures.
Nevertheless, one of the key ways to avoid such recurring issues is to ensure the marking needles that are used are of high quality, precision engineered, durable, and compatible with the machine. At our company, we manufacture durable marking needles for pneumatically actuated marking machines, electric dot matrix markers, and scribing machines. Zixu marking needles range from 95 HRA tungsten steel marking needles to titanium plated marking needles for longer lifetime, and even diamond tipped marking needles for extreme hardness. We produce over 50,000 sets per year, which gives us the trust of nearly half of China’s market and one third of the world’s market, even other manufacturers in the industry.
The failure rate of pneumatic marking machines can be controlled and reduced significantly through proper systematic inspection and regular servicing. In the instance the issue persists, seeking the original equipment manufacturer’s technical support is a reasonable next step.
Recommended Products




