How to adjust the resistance of thin film and thick film resistors?
In the design of certain MEMS devices, adjustable resistors are often required. On board-level circuits, the resistance of chip resistors can be adjusted using potentiometers. But how are chip-level thin-film resistors and board-level thick-film resistors adjusted?
A common method is to use lasers to tune the resistance of thin and thick films. The principle of laser trimming is to use an extremely fine laser beam to strike a chip resistor, cutting it through the vaporization of the resistive material. The laser beam cuts the chip resistor according to a pre-programmed computer program, changing the resistor’s geometry and thus its resistance value. As the laser cutting process progresses, the resistance value continuously approaches the target value. Simultaneously, a measuring circuit monitors the change in resistance value in real time. Once the chip resistor reaches the target resistance value, the laser beam is turned off, thus completing the laser trimming process.
Laser trimming technology has wide applications in various fields such as communications, medicine, materials processing, scientific research, military, and industry because its characteristics make it suitable for diverse needs. It is used in current sensors, thick-film circuits, thin-film circuits, proximity switches, and many other industries.
Laser trimming requires a laser trimming machine. Currently, there are three main types of laser trimming machines on the market based on usage requirements: thick film laser trimming machine, thin film laser trimming machine, and ultra-low resistance laser trimming machine.
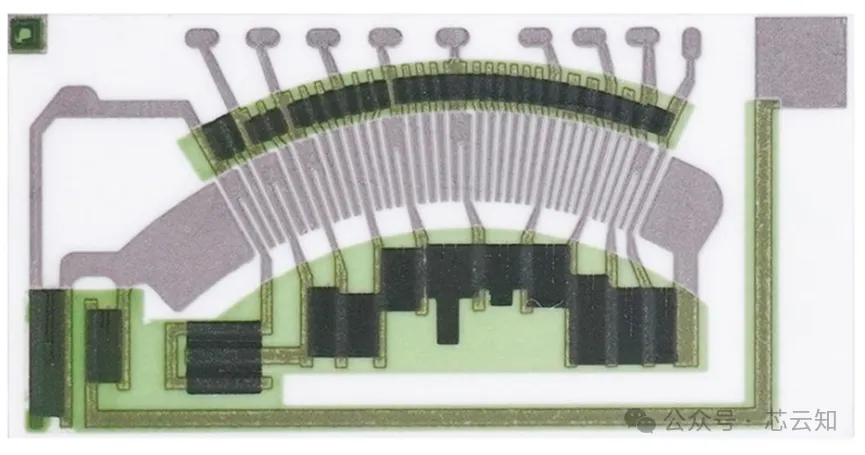
(1) Thick film laser trimming machine
The main focus is on trimming the resistance of sheet-type thick-film resistors, including resistors ranging from 1mΩ to 10MΩ based on thick-film manufacturing processes. Infrared lasers and green lasers are commonly used for laser trimming. Due to the low precision and large linewidth of thick-film resistors, the diameter of the thick-film laser beam is often greater than 40μm. The main method involves changing the geometry of the thick-film resistor by cutting.
(2) Thin-film laser trimming machine
The main focus is on trimming the resistance of chip-type thin-film resistors, including resistors ranging from 1mΩ to 10MΩ based on thin-film manufacturing processes. Green lasers and ultraviolet lasers are commonly used for laser trimming. Since thin-film resistors are often deposited on wafers via PVD, the linewidth is typically small, usually 1~10μm, with a spacing of 3~10μm. Currently, the highest-end laser beam diameter is 3μm, and trimming is mainly achieved by cutting the parallel resistor lines.
(3 ) Ultra-low resistance laser trimming machine
It mainly focuses on adjusting the resistance of alloy-type chip ultra-low resistance resistors, including resistors ranging from 1mΩ to 1Ω based on the alloy chip resistor manufacturing process; infrared lasers are commonly used for laser resistance adjustment.
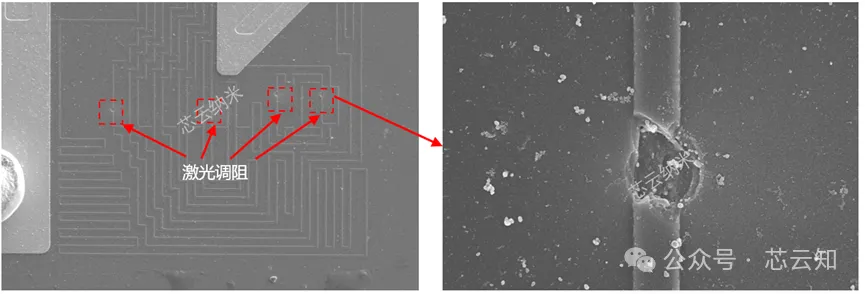
What are the advantages of laser trimming?
1) High adjustment precision – improving the accuracy of products to be processed
For example, resistors with initial values of 72Ω, 82Ω, 89Ω, etc., can all be adjusted to the set target value (e.g., 100Ω) using laser trimming. In functional adjustment applications, some electronic modules, regardless of their initial output values such as 3.8V or 6.2V, can be quickly adjusted to the required target value (e.g., 5V) using a laser trimming machine.
2) Fast adjustment speed – with higher production capacity
Compared to other adjustment processes, such as manual resistor replacement and potentiometer adjustment, laser trimming, thanks to its high-speed real-time measurement and automated program control technologies, takes only tens of milliseconds to process a single resistor. This is several times or even more than ten times faster than other trimming methods, significantly reducing labor costs and offering a major advantage, especially in mass production.
3) Capable of meeting the production needs of smaller components – reducing the size of processed products
The demand for circuit miniaturization is constantly increasing, especially in the consumer electronics field. Because laser beams can be focused to 35µm or even 10µm during laser processing, certain microcircuits can only be achieved using laser trimming technology, which other processes cannot handle. At the same time, miniaturization means that more products can be produced on the same substrate, reducing the unit cost of the products.
4) Automated, multi-functional testing platform
Laser trimming machines not only enable trimming of products, but also serve as multifunctional testing platforms in practical applications. They can perform automatic testing, selective trimming, non-conforming product calibration, and data analysis on overall trimmed products, providing strong support for users in the product manufacturing process.
5) High reliability and high degree of automation
The laser trimming machine uses a dedicated laser, resulting in excellent cut stability after trimming with virtually no resistance drift, ensuring product stability after trimming. It can also be equipped with automatic loading and unloading fixtures to achieve full automation of the laser trimming process.
END
The reprinted content represents only the author’s views.
This does not represent the position of the Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Edited by: Xiaoshuai
Editor: Six Yuan Fish
Submission email address: weixin@semi.ac.cn
Previous Recommendations
- Advances have been made in the research of biomimetic overlay neuron models and learning methods at the Institute of Semiconductors.
- Significant progress has been made in the field of inverted perovskite solar cells.
- Why are copper used as the interconnect metal in chips?
- What exactly is 7nm for chips?
- Silicon-based integrated photonic quantum chip technology
- How anomalous is the quantum anomalous Hall effect? It may bring about the next information technology revolution!

