General troubleshooting procedures for abnormal laser welding of lithium batteries (applicable to top cover welding and sealing nail welding)
Laser welding is a critical process in lithium battery manufacturing, and currently, apart from destructive metallographic inspection, there are no effective means to monitor welding quality online. Any problems in laser welding can lead to batch defects.
This article by Bu Yan summarizes a general handling process for laser welding anomalies in lithium battery

Laser welding system and schematic diagram
1. Preliminary diagnosis and isolation
Shutdown confirmation : Immediately stop the production line, isolate the abnormal batch of batteries , and prevent defective products from flowing into the next process.
Phenomenon Record :
Record the types of defects (bursts, pinholes, cold welds, cracks, etc.) and their locations.
Take photos of macroscopic and microscopic defects and compare them with the morphology of normal weld beads.
2. Key factor screening (5M1E analysis method)
Equipment (Machine) :
Check the stability of the laser output energy: use an energy meter to measure whether the power fluctuation is ≤3%.
Check for optical system contamination: focus lens/collimating lens melt damage, clean or replace the lens (follow SOP).
Verify the focal position: Confirm the focal offset through a spark test or blade light transmission test.
Materials :
Confirm the fit clearance between the top cover and the aluminum shell: a clearance greater than 0.1mm can easily lead to poor soldering.
Check the surface condition of the material: oxide layer, oil stains or uneven coating will affect the absorption rate.
Method :
Check welding parameters: power, decoking amount, and speed to ensure they are within the specified range.
Verification of waveform design: Insufficient duration of the heat conduction welding stage (10–10 W/cm²) can easily lead to cracks.
Environment :
Monitor the purity and flow rate of the protective gas: Impurities in argon gas can cause porosity.
Confirm the negative pressure value of the dust removal system to prevent smoke and dust from interfering with the optical path.
Man :
Check the operation records: whether lens replacement and clamp cleaning were performed in accordance with the SOP.
3. Single-factor validation experiment
Small-batch trial welding was conducted for suspected factors (such as defocusing amount ±0.2mm, power ±50W).
Metallographic inspection of penetration depth/penetration width: confirm whether it is within the specifications (effective penetration depth ≥ 300μm).
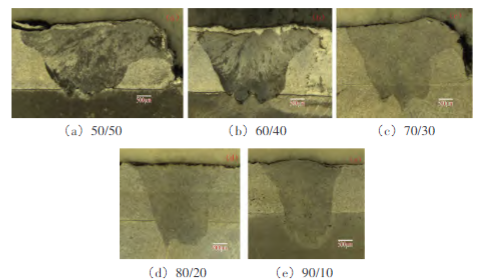
Weld morphology at different energy ratios
4. Root cause identification and correction
Energy attenuation : Clean/replace optical components, calibrate the optical path.
Parameter offset type : Optimize power density window (10–10 W/cm²) and extend slow cooling time.
Material matching : Adjust the top cover structure (e.g., add stress relief grooves to the sealing nails).
5. Long-term measures
Establish predictive maintenance: Regularly check lens transmittance and laser BPP value.
Standardized parameter management: unifying the focus position and trajectory drawing method for multi-station equipment.
Personnel training: Certification is required for key operations such as focusing lens replacement and CCD focusing.
6. Frequently Asked Questions Quick Reference Table
Note: Repair processes should be handled with care (e.g., filler wire welding is limited to 3 times) to avoid secondary damage.
In addition to the above-mentioned anomaly handling procedures, there is another very important step for lithium battery mass production lines: identifying the scope of risky products . Generally, after finding the root cause of the problem, the scope of risk is determined based on the changes in the manufacturing process, using a tiered disassembly approach to prevent defective products from leaking out.
This process achieves rapid response to welding anomalies through systematic fault diagnosis and closed-loop control. Consolidating empirical data and continuously optimizing parameter windows improves process stability, providing a reliable guarantee for high-quality battery manufacturing.
The above content is based on my daily work, communication, and literature review. Due to my limited ability, there may be omissions in the viewpoints presented. I welcome colleagues in the industry to actively exchange ideas and make progress together!
Reference materials (available for download from the lithium battery decoding database):
1. Research on the characteristics of laser welding of aluminum alloy rings for energy storage batteries, Chen Jianhao
2. Research on Laser Welding Technology for Automotive Power Battery Cover Plates, Geng Libo
Original Title: General Handling Procedures for Lithium Battery Laser Welding Anomalies (Applicable to Top Cover Welding and Sealing Nail Welding)

