FIVE Type of Commonly Laser Welding Applications for Manufacturers

Laser welding machines are extremely popular nowadays and are used in a wide range of industries. Despite their higher initial cost, many industry users favor laser welding machines due to their stable welding quality, ease of operation, high reliability, low failure rate, simple structure, and ability to easily achieve automation. Below, I will introduce some of the most common laser welding applications.
Major Laser Welding Applications
Laser welding is widely used in industries like automotive, shipbuilding, electronics, battery manufacturing, and medical devices. It enables efficient, precise welding of frames, panels, battery components, damaged parts, and implantable metals using handheld, robotic, or CNC systems.
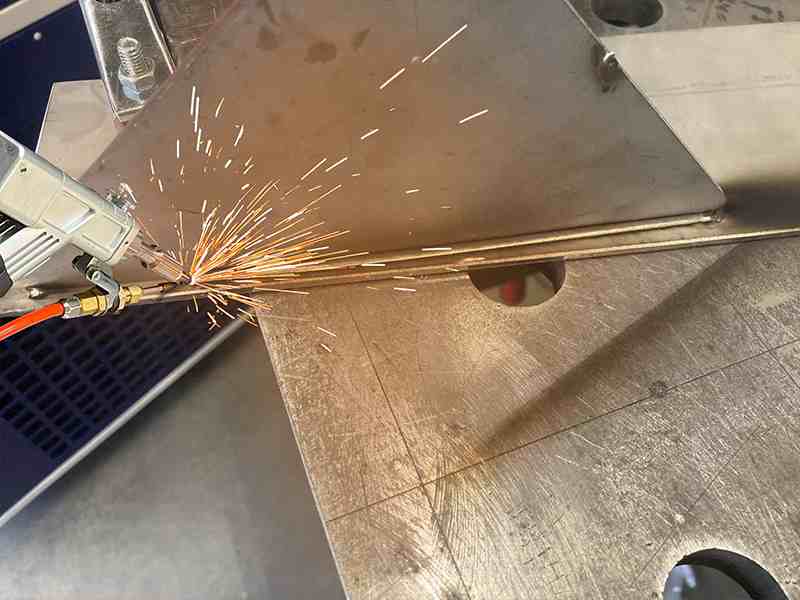
Frame & Structure Welding

Many products use a high-strength metal skeleton to ensure structural integrity and different surface materials, such as lightweight metals and plastics, to reduce weight and manufacturing costs. This type of structure is used in everything from inexpensive household appliances to automobiles, airplanes and ships.
Handheld fiber laser welding machines have become popular for welding metal structures that do not require high strength or consistency, such as aluminum alloy door frames. With this type of welder, the torch automatically controls the wire feeder and air blow. Users simply press the trigger and drag the torch to complete the job.
Laser welding robots are often used for heavy-duty skeleton or structural welding. Since the structure is simpler than that of a conventional metal-arc welding (MAG) setup, the welding torch, gas tube, wire feeder, and other components can be easily mounted on the robot for motion control. These robots are currently used in many automotive and advanced electronics manufacturing industries.
Body Welding (Panel)
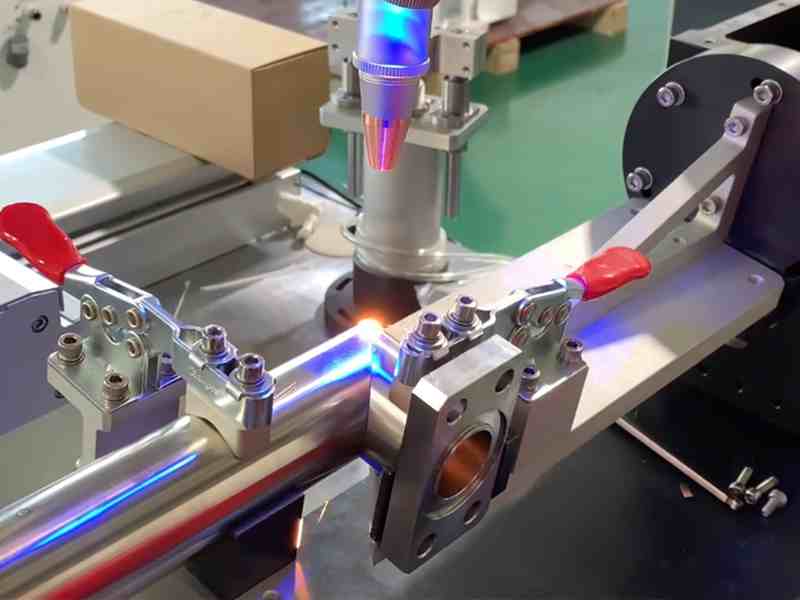

As mentioned above, some products, such as automobiles, airplanes, and ships, use metal panels with different frames for their housings. These metal bodies and panels are also ideal for laser welding.
In the shipbuilding industry, where the size and displacement of each vessel varies, handheld laser welding machines are commonly used to weld the vessels’ hulls and remove the oxidized layer from the welds using the torch’s weld mark cleaning function. In addition, for some equipment on board that needs to be rigidly mounted and sealed, such as watertight compartment plate seams, spindle sealing flanges, etc., in addition to the use of rivets and screws to mechanically fasten the workpiece, sealing using a hand-held laser welding is also used.
Laser welding is widely used for many key automotive components, including engines, gearboxes, generators, compressors, solenoids, connectors, valves, pipes, and circuit boards. There are four main types of laser welding: flexible handheld, precision using electron microscopes, and automated using CNC systems or robots.
In the automotive industry, vehicle housings are often fitted with sheet metal parts directly to reduce repair and replacement difficulty and cost. Laser welding is commonly used for roof housings, underbody panels, windows, doors, tailgates, and other body parts.
In the field of consumer electronics and home appliances, metal shells are used for a variety of components and undergo laser welding for products such as cell phones and refrigerators. These products are typically welded using CNC multi-axis laser welding to ensure consistent weld width and quality. This process can also be combined with grinding and other techniques to achieve optimal aesthetic results.
Lithium Battery Welding (EVs & ESS)
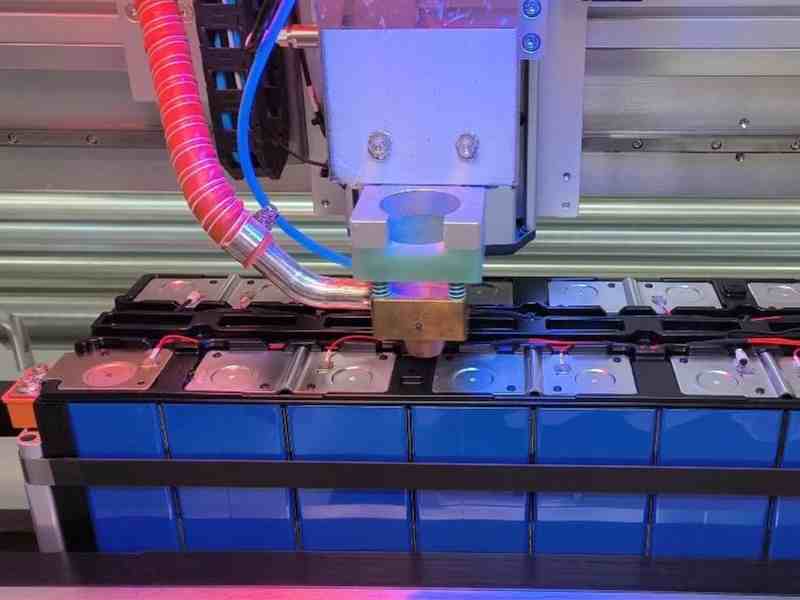

Due to environmental and technological advances, electric vehicles (EVs) and energy storage systems (ESS) based on lithium batteries which are gaining popularity today, require more welding process than lead-acid batteries due to a number of characteristics. Since Li-ion batteries are inherently unstable, when used in large quantities they need to be packed with a battery management system (BMS) that matches their performance in terms of capacity and internal resistance. Whether the battery cells are brand new or require repair, they must be rematched and then packed into a battery pack. Therefore, in addition to the welding of the battery cell itself and the positive and negative electrodes, the laser welding of the electrode lugs in the PACK stage will require more welding.
Repair Welding

Laser welding is now widely used to repair molds damaged by wear and tear or collisions, or turbine blades cracked by collisions. Typically, laser welding can be used to fill and repair such defects by quickly melting solder, such as tin, to extend the service life of the part.
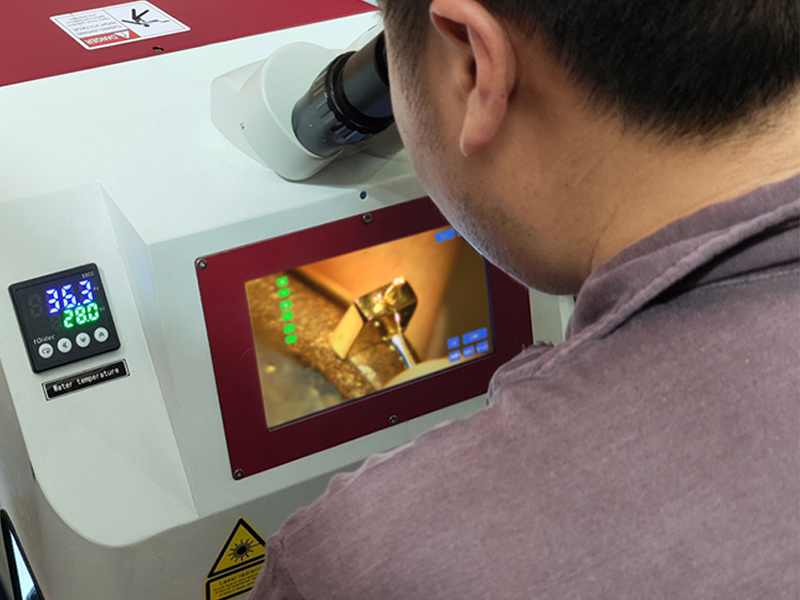
In addition, when carrying out precious metal repair welding of jewelry, usually to ensure the purity of precious metals such as gold, silver, platinum, palladium, etc., the repair is usually carried out using material-free laser welding. By melting the base material in the welded area with a high-energy laser beam, solderless repair welding is realized.
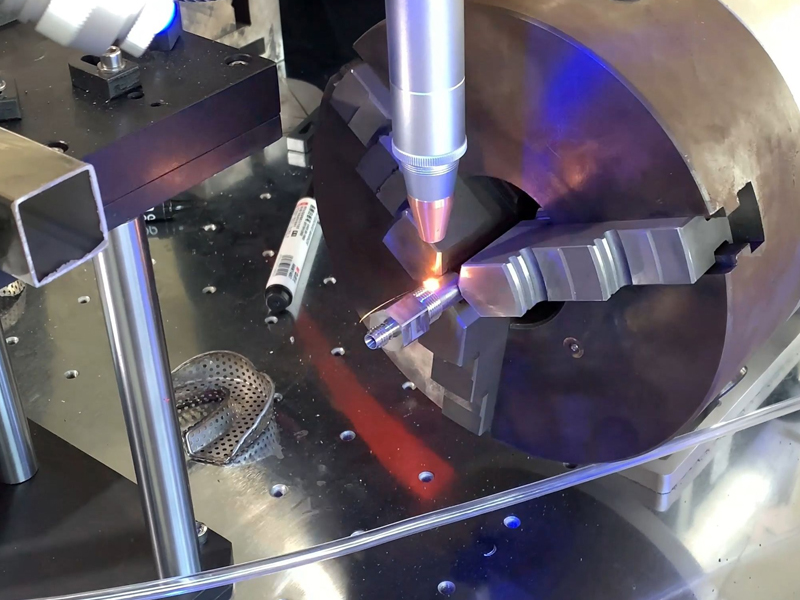
Implantable Medical Device Welding
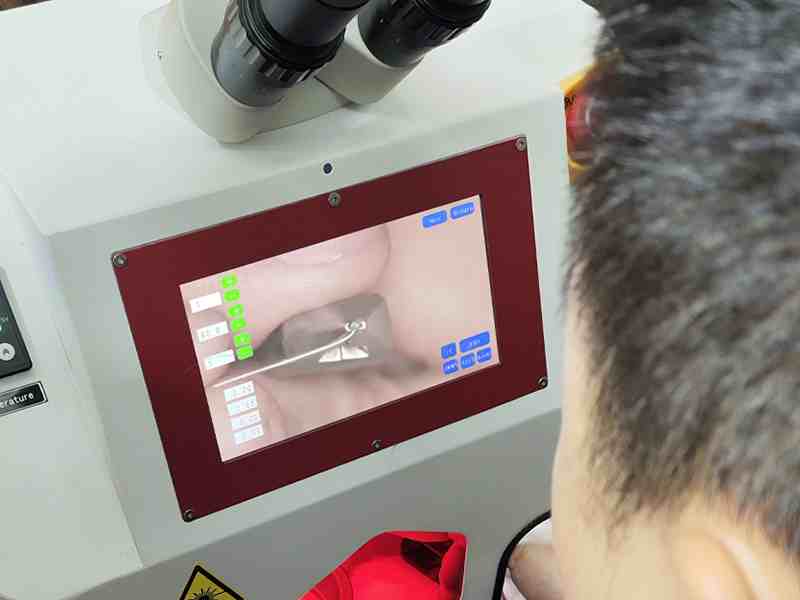
The medical field shares some welding needs with other industries, such as skeletons, housings, and components, as mentioned previously. Here we will illustrate the application of laser welding of human implanted metals. These metal objects are widely used in orthopedics, dentistry, cardiovascular surgery, neurosurgery, and other fields.
Commonly used metal materials for human implantation include titanium, nickel-titanium, stainless steel and cobalt-chromium alloys, of which titanium has become the optimal choice for this application due to its biocompatibility. Because conventional solder, such as tin, is more likely to cause rejection, we usually use high-energy laser material-free welding in human implantation of metal. Some customers in the industry call this laser self-melting welding.
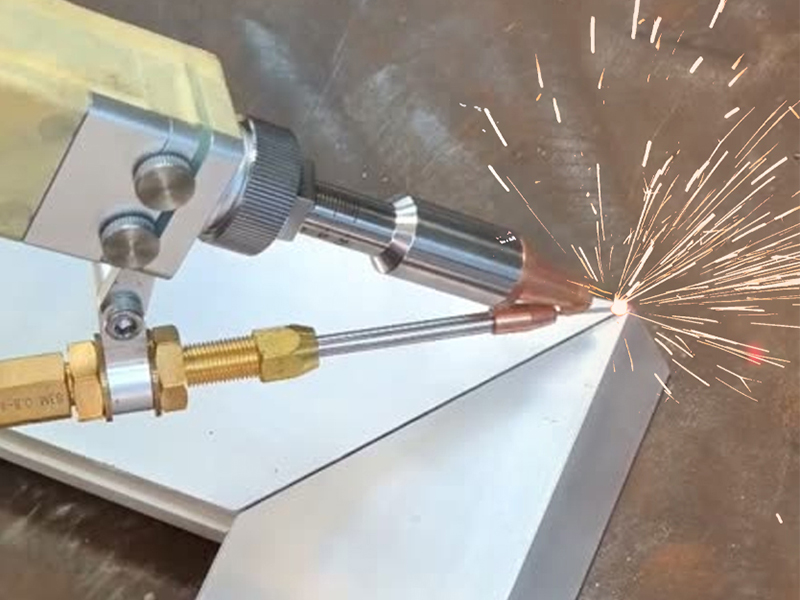
Can Laser Welding Join Dissimilar Metals?
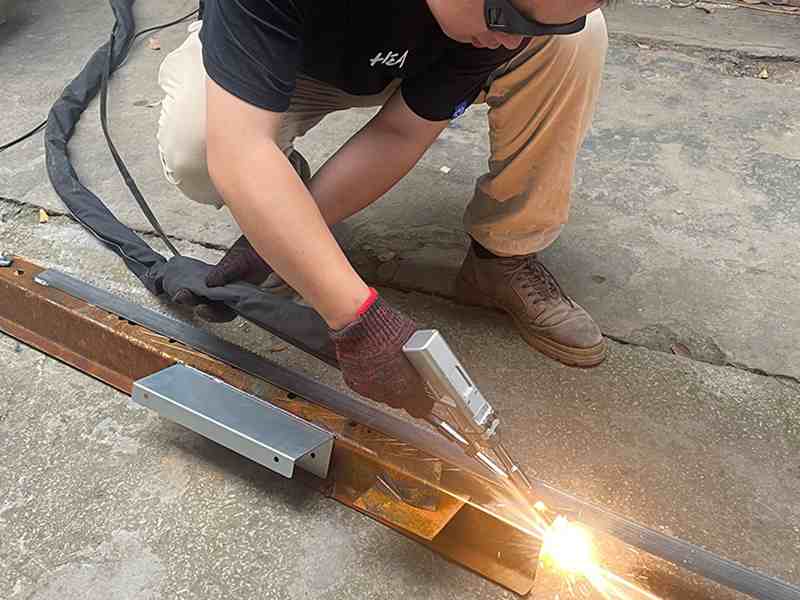

The high-power fiber laser that we use melts the metal locally and forms a weld seam, which welds dissimilar metal materials together without the use of solder. Due to differences in physical and chemical properties, welding dissimilar metals requires paying special attention to factors such as the material’s coefficient of thermal expansion, melting point, and thermal conductivity.
Titanium and aluminum, for example, are commonly used in the aerospace industry. However, they have large differences in their melting points and thermal conductivity, and are therefore prone to producing intermetallic compounds (IMCs) during welding. These IMCs affect the performance of the welded joint. In this case, we use a QCW fiber laser, which provides a narrower beam and more precise heat input control. This reduces the hot zone range and the probability of intermetallic compound formation.
Can Lasers Weld Non-metal Materials, Such as Glass or Plastic?

Glass is a transparent, brittle material that is difficult to weld directly using conventional methods. However, transmission welding can be used. In this technique, the laser passes through the transparent upper material, heats up the lower material, and melts it to create a connection. The challenges of laser welding glass include overcoming its high reflectivity and high coefficient of thermal expansion.
For this purpose, it is often necessary to use the ultra-short pulse width of ultra-fast infrared picosecond lasers, supplemented by burst mode for more precise heat control. The high cost of such systems means that glass welding technology is still in the exploratory phase and is not yet widely available to industrial users.
Welding plastics also requires the use of transmission welding technology. We use a 1064nm fiber laser that passes through the transparent upper layer of PMMA and melts the lower layer of PC, ABS, LDPE, HDPE, PVC, Nylon, PS and other plastics to form a weld. However, the use of laser welding of plastics is also in the exploratory stage, as it requires a high degree of thickness and actual light transmission. The welding of both plastics and glass has not yet become a popular process that can be applied in large quantities, and we are currently supplying only a few universities for research purposes.
Looking for a Laser Welder But Are Still Undecided?

Currently, Zixu primarily manufacture welding machines that use fiber, QCW fiber, and YAG lasers for various industries. Our product line includes portable and handheld laser welders, as well as CNC, multi-axis, platform, and robotic laser welding machines.
Are you looking for a laser welding machine supplier that offers excellent technical support and after-sales service? If so, please contact us.
Recommended Products




